When symptoms like cold feet, leg pain when walking, or wounds that won’t heal appear, getting the right diagnosis matters. Your body sends signals when blood flow through your arteries and veins isn’t working properly. Vascular specialists have the tools to pinpoint exactly what’s happening.
Understanding how vascular doctors diagnose circulation problems in your cardiovascular system helps you feel more confident walking into that appointment.
Signs You Might Need a Vascular Evaluation
Vascular specialists focus on blood vessel health throughout your body, treating conditions affecting arteries and veins like peripheral artery disease and deep vein thrombosis.
Cold extremities that don’t warm up deserve attention. Leg cramps appearing with walking, then disappearing with rest, indicate restricted arterial blood flow.
Signs of poor circulation include numbness in feet, one-sided swelling, discolored skin, and slow-healing wounds. These symptoms suggest inadequate oxygen delivery through blood vessels.
These warning signs develop gradually. Early detection of vascular circulation problems provides more treatment options and better outcomes.
What to Expect During a Vascular Check-Up
Your first appointment starts with conversation. Specialists ask about symptoms, onset timing, and aggravating factors. This medical history reveals important patterns.
How vascular doctors test blood flow depends on lifestyle factors like smoking, family history, and chronic conditions like diabetes. The specialist examines pulse points, checks skin temperature and color, and observes movement. These observations reveal circulation issues before imaging.
The physical exam is straightforward. You might walk down a hallway for gait assessment. They check for swelling or tenderness in your legs and feet. This builds a picture before testing begins.
How Vascular Specialists Assess Blood Flow
Once your specialist understands your symptoms, they move to diagnostic testing. These circulation tests for vascular health range from quick and simple to more detailed imaging.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Test
The ankle brachial index test is usually the starting point. It’s noninvasive with immediate results.
A technician measures blood pressure in your arms and ankles using a standard cuff and Doppler device. They compare these numbers to assess lower extremity blood flow. The process takes about 15 minutes.
Lower ankle pressure compared to arm pressure suggests peripheral artery disease. This simple test catches many cases early, allowing for timely PAD treatment before complications develop.
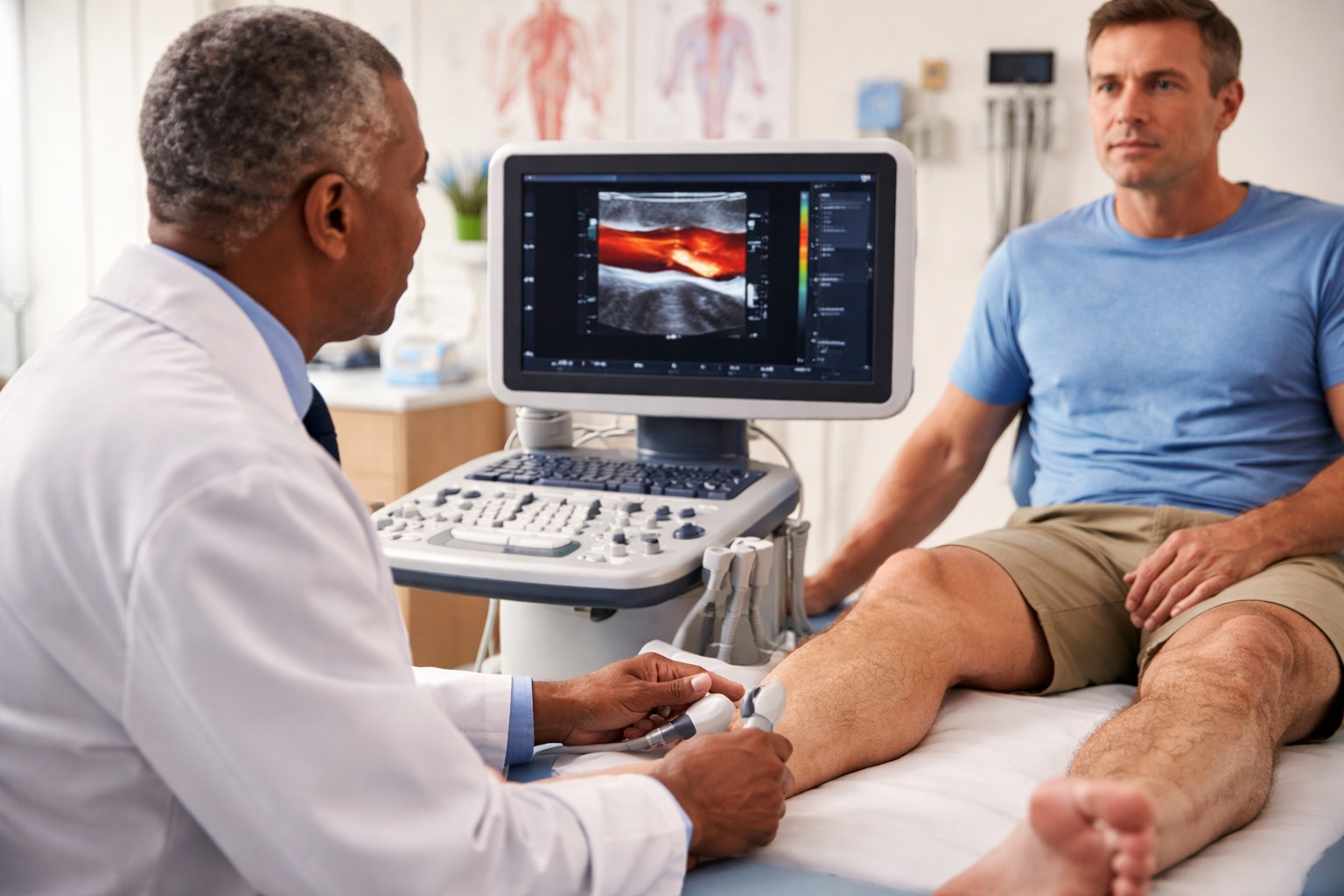
Doppler Ultrasound & Duplex Imaging
When specialists need to visualize blood vessel activity, vascular diagnostic imaging becomes essential. Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to create real-time circulation pictures.
The technician applies gel and moves a transducer over examination areas. You’ll hear whooshing sounds as blood moves through vessels.
These circulation tests for vascular health reveal blockage locations, severity, and flow direction. Duplex imaging combines traditional ultrasound with Doppler technology for structural and flow data. No needles, no radiation.
Angiogram, CTA & MRA
Ultrasound sometimes lacks sufficient detail for complex blockages or procedure planning. More detailed imaging fills this gap.
Traditional angiography inserts a thin catheter into an artery, injecting contrast dye during X-ray imaging. It provides detailed arterial system pictures and enables same-session treatment. Most patients go home the same day.
CT angiography (CTA) and MR angiography (MRA) offer similar detail without catheters. CTA uses CT scanning with IV contrast. MRA uses magnetic fields, often without contrast. Both create three-dimensional circulation maps for thorough analysis.
These tests help specialists plan optimal treatment approaches, whether medication, lifestyle modifications, or minimally invasive procedures.
Additional Diagnostic Tools
Specialists have other tools for specific situations. Segmental pressure measurements check circulation at different leg points, pinpointing blockage locations. Plethysmography measures leg volume changes with each heartbeat, showing extremity blood flow efficiency. Treadmill stress tests reveal exercise-induced problems, particularly useful for diagnosing claudication.
Specialists select tests based on symptoms and what information they need. Not everyone needs every test. The goal is efficient, accurate information for prompt treatment.
Next Steps After a Diagnosis
Vascular specialists create personalized treatment plans for blood vessel disorders.
Treatment often starts with medication. Blood thinners prevent clots. Cholesterol-lowering drugs slow arterial plaque buildup. Blood pressure medications reduce vessel wall strain. These work best with lifestyle modifications.
Exercise programs designed for vascular patients improve symptoms significantly. Walking regimens develop collateral circulation around blockages. Dietary changes reduce inflammation. Smoking cessation is essential.
When arterial blockages are severe or venous conditions impact quality of life, procedures become necessary. Angioplasty opens arteries. Stents maintain patency. Bypass surgery creates new routes. Vein treatments address varicose veins and insufficiency.
Early peripheral artery disease diagnosis prevents limb loss and stroke. Prompt DVT treatment prevents pulmonary embolism and long-term complications. Early intervention improves vascular health outcomes.
FAQs About Vascular Diagnosis
How long does a vascular test take?
Individual tests take 15 to 45 minutes. Ankle-brachial index tests complete in 15 minutes, while duplex ultrasounds require 30 to 45 minutes. Complex imaging like CTA or MRA typically needs about an hour including preparation.
Are vascular tests painful?
Most vascular diagnostic tests are painless. Ultrasound and Doppler studies involve only gel and gentle transducer pressure. Catheter-based tests like angiography use local anesthesia, causing pressure sensations but not pain.
Can lifestyle changes improve circulation without surgery?
Yes. Many peripheral artery disease patients see significant improvement through lifestyle modifications. Walking programs, smoking cessation, dietary changes, and medication management reduce symptoms and slow progression. Specialists determine whether conservative management works or intervention is necessary.
Taking Control of Your Vascular Health
Circulation problems in your arteries and veins respond well to early treatment. The diagnostic process provides essential information guiding your care.
If you’re experiencing vascular symptoms, don’t wait. Schedule an evaluation with a vascular specialist at Prime Vascular Care for accurate assessment and appropriate treatment recommendations.