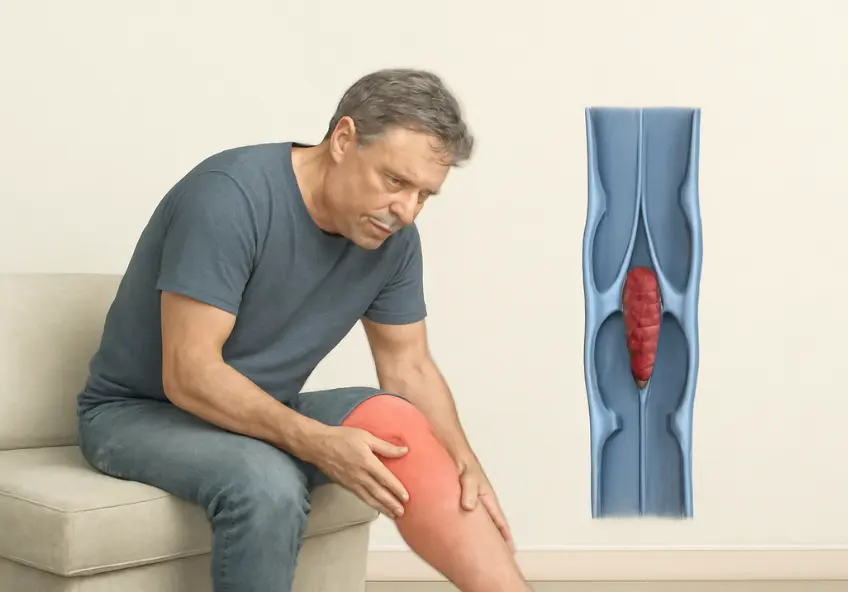
Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within a deep vein of the body, typically in the legs. It does not seem like a serious circulation issue at first, but there is a risk of what can occur subsequently. If a clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can result in a pulmonary embolism which is a medical emergency and can be fatal.
Understanding what deep vein thrombosis is, the risk it poses and what can be done to mitigate the issue is important. With the proper deep vein thrombosis treatment and lifestyle changes many complications can be avoided simply by understanding the risk factors.
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
DVT starts when blood flow begins to stagnate in a specific area of a vein. These clotted blood pone veins are neither deep inside the muscles nor visible on the surface level. Some people’s legs might experience swelling, uneasiness, pain and discoloration, but not everyone displays noticeable symptoms. It is this lack of symptoms that makes the condition very dangerous.
When a clot becomes detached and lodges in the lung, the resultant pulmonary embolism poses the greatest danger. This complication is life-threatening and needs to be treated immediately, as it can be accompanied by sudden chest pains, fainting, or even shortness of breath.
Why Is DVT Considered Dangerous?
DVT can cause the legs to swell, but it is the complications that truly pose a grave danger. The most serious of which is pulmonary embolism. A lot of patients experience the long-term effects of post-thrombotic syndrome, which results in a leg with a clot that becomes painful, discolored and swollen for many years.
Recurrence is another problem. After suffering from DVT, the likelihood of acquiring another clot is much greater. This is why the vascular associate emphasizes the need for prompt treatment and diagnosis, like for other vascular illnesses such as arterial disease.
Who Is Most at Risk?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing DVT. These include lifestyle habits, existing vein problems and underlying health conditions.
- Prolonged immobility, such as during long flights or after surgery, slows circulation and allows clots to form. This is why many doctors encourage patients to prevent DVT during travel with simple steps like moving regularly or stretching.
- Age and genetics play a role, with older adults and those with a family history of clotting disorders being more susceptible.
- Vascular conditions such as peripheral arterial disease can indicate poor circulation, which increases the risk of clotting and requires immediate specialized treatment, such as peripheral arterial disease treatment.
- Lifestyle choices, including smoking, obesity and lack of exercise, can all contribute to DVT.
Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
One of the challenges with DVT is that symptoms may not always be obvious. When they do appear, they typically affect only one leg.
- Sudden swelling, usually in the calf
- Pain or cramping that worsens when standing or walking
- Red or bluish skin color on the leg
- A warm sensation around the affected area
If these signs are accompanied by chest discomfort or difficulty breathing, immediate medical attention is critical, as these could be signs of a pulmonary embolism.
How Doctors Diagnose DVT
DVT’s more clinical aspects are initiated by a physical examination. This is most often followed by confirming tests for the presence of blood clots, the most common of which is an ultrasound. A D-dimer blood test may help assess the level of clot formation as well.
In difficult situations, advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or venography may be warranted. At Prime Vascular Care, we don’t just focus on treating visible vein issues but also address related conditions like varicose veins, carotid artery disease and other vascular concerns ensuring patients receive complete, individualized care.
Choose the Best Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment for Your Health
Explore your treatment options and get expert advice from our vascular surgeon.
Treatment Options for Deep Vein Thrombosis
The goal of therapy is to ensure the clot does not grow larger, does not travel to the lungs and the risk of future clots is minimized.
Starting therapy, the first option is the use of anticoagulants, or blood thinners. These medications help to prevent the enlargement of the existing clot and the formation of new clots. In other situations, especially when the clot is more proximal, some form of direct clot removal or clot breakdown procedure, which is minimally invasive, may be performed.
Doctors may also recommend wearing compression stockings. These improve circulation in the legs and help reduce the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome. They are widely used in both deep vein thrombosis care, showing their value across multiple vein conditions.
Preventing DVT Before It Happens
Because of the serious complications, prevention plays a central role in managing DVT.
- Continue to exercise regularly and avoid sitting down for a long time.
- Avoid dehydration and drink water to enable smooth circulation.
- If your doctor orders it, wear compression stockings.
- Get up and walk around during long trips to stretch.
- If you suffer from PAD or carotid artery disease, you should follow the doctor’s advice.
Some lifestyle adjustments can also be beneficial. For instance, PAD, engaging in consistent physical activity and maintaining your weight improves the blood vessels and diminishes the likelihood of forming a clot.
The Importance of Awareness
People often hear of deep vein thrombosis as a condition ‘linked to silence’ as it can develop without obvious signs. This means it’s a condition that can go undiagnosed. The reality is that many patients are often diagnosed when it is considerably complicated. This is why marked awareness is important. If people knew how to identify the signs of the condition when they occur, they could have a better fighting chance of surviving.
Awareness is essential and has a wide range of implications when it comes to other blood vessel ailments as well. For example, carotid artery screening helps identify stroke risk before symptoms appear and learning about varicose vein prevention can help people avoid circulation issues that raise clotting risks.
Final Thoughts
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition that should never be underestimated. Though it can start quietly, complications can arise from ignoring it. Risk can be greatly reduced with early diagnosis, effective treatments and a sensible regimen.
The most proactive approach, in your case, would be to visit a vascular specialist. Rest assured, whether it’s managing deep vein thrombosis, seeking varicose vein treatments, or preventing complications from abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), expert care can make a significant difference in long-term health.
Taking action today is the key to preventing serious complications tomorrow.