Have you ever experienced unexplained swelling or the occasional aching of a leg? Most of the time, you write it off as a muscle strain or fatigue, but it can be more than that. One of the conditions that tends to be taken for granted until it demands attention is called Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg, which can lead to life-threatening conditions if left unattended. It is of utmost importance to know how to recognize the symptoms of DVT in the leg and how to treat it. This would include understanding the causes and being educated about the DVT treatment. Let’s go through it step by step.
Signs and Symptoms of DVT
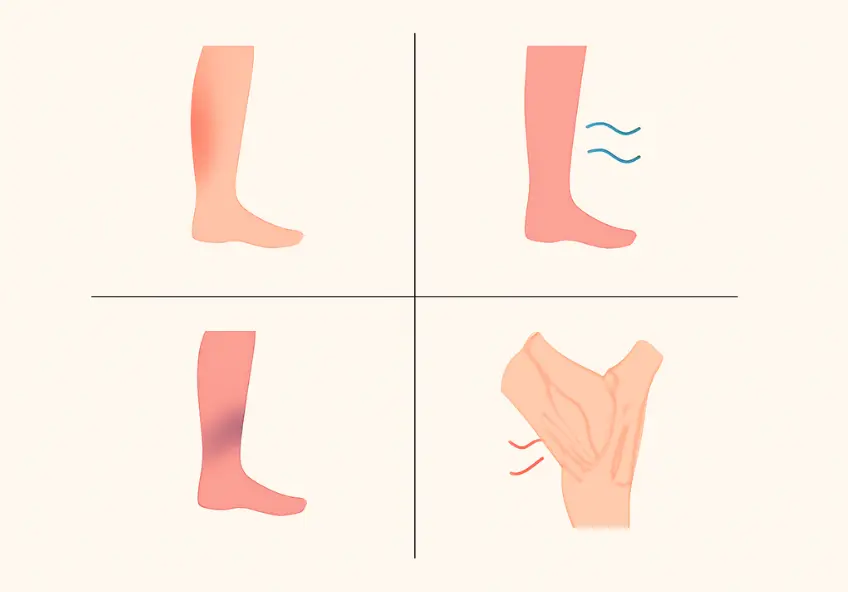
Typically, the body does show signs of DVT, but they can be difficult to recognize. Some people show only slight discomfort, while others exhibit more apparent changes. The most common DVT signs and symptoms are:
- Swelling, usually sudden in one leg only.
- Pain or tenderness, especially in the calf or thigh.
- Discoloration of the skin, reddish or bluish, in the area.
- The affected leg is warmer than the other.
- The leg feels heavy and tired.
Not everyone will have all of these symptoms together. Sometimes, it is just the swelling, or just some pain that is persistent. However, these signs and symptoms of DVT should be attended to, particularly if there are multiple symptoms present.
Why Does DVT Happen?
So why do these clots form in the first place? The most common DVT causes usually come due to poor circulation or damage to the veins. Blood flow can be slowed by prolonged periods of inactivity, such as during long travels, during recovery after surgery, or when wearing a cast.
More causes can include:
- Vein injuries or surgeries
- Certain medications, such as birth control or hormone therapy
- Obesity or heart disease
- A family history of clotting problems
Many people do not realize that having varicose veins also increases your risk. This, in addition to the cosmetic aspects, should encourage people to take steps in varicose vein prevention.
How Doctors Diagnose DVT
A DVT diagnosis will often start with an ultrasound. This test, which is relatively simple by medical standards, evaluates circulation and detects blockages in veins using sound waves. If necessary, blood tests can also be performed to identify clotting.
Early detection of DVT is crucial. And while a clot in the leg might cause discomfort, a potentially life-threatening pulmonary embolism can occur if the clot travels to the lungs. Hence, it is understandable that medical practitioners will not take risks in such situations.
Treatment and Medications
Once DVT is confirmed, it is essential to treat symptoms, prevent progression and stop new clot formation. The first line strategy is prescribing blood thinners. While these DVT medications do not dissolve the clot, they do stop it from growing while it is being resolved intrinsically.
In some instances, DVT specialists do prescribe clot-dissolving medications, although it is mostly reserved for emergencies.
In addition to medications, compression stockings are recommended to improve circulation, prevent swelling and relieve discomfort. These stockings are quite basic, but they significantly improve the recovery process.
Besides medications, other preventive measures are of great value, including maintaining an active lifestyle, taking short walks after prolonged sitting, staying hydrated and controlling body weight. For patients with existing venous insufficiency, advanced vein treatments may be indicated for additional symptomatic relief and improved circulation.
Choose the Best Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment Option for Your Health
Explore your treatment options and get expert advice from our vascular surgeon.
Can DVT Be Prevented?
You can adopt a few simple routines or habits to reduce the risk of developing DVT:
- Engage in regular movement, particularly during extended periods of flying or driving.
- If your work involves extended hours of sitting, do stand up and move during your breaks.
- If your healthcare provider suggests it, use compression stockings.
- Blood becomes thicker when you are dehydrated, so make sure to drink plenty of water.
- Maintain a regular physical activity and balanced nutrition plan.
- If you are on certain drugs or prescriptions, consult with your physician.
Most of these steps are also useful in preventing varicose veins which shows how important these simple habits are for circulation in your legs.
When to See a Doctor
You might think that leg discomfort and swelling is harmless but it is always better to be clear. If there is continuous swelling, pain or some discoloration, do not hesitate to reach out.
Most importantly, do not delay getting help if you suddenly develop shortness of breath, pain in the chest, or coughing blood. A blood clot could be in the lungs and it is a medical emergency that must be treated right away.
At Prime Vascular Care, we believe that vascular health should be correlated with other body systems in order to create a custom treatment plan that encompasses all of an individual’s needs–along with the treatment of varicose veins, we also treat other vascular-related disorders such as abdominal aortic aneurysm and carotid artery disease.
Final Thoughts
Recognizing the symptoms of DVT in the leg should not be to instill fear, but to empower you. Simply knowing what to watch for can help you take the proper actions and prevent more serious issues.
With the right treatment, the condition can be managed with medications, compression stockings, or through more invasive forms of vein care. Even more, small, simple actions like remaining active and taking steps to prevent varicose veins will greatly reduce the risk.
The bottom line is simple: pay attention to your body and any changes in your condition and do not disregard any signs that there could be a problem. A quick visit to your doctor can greatly help.